Wireless network security primarily protects a wireless network from unauthorized and malicious access attempts. Typically, wireless network security is delivered through wireless devices (usually a wireless router/switch) that encrypts and secures all wireless communication by default. Even if the wireless network security is compromised, the hacker is not able to view the content of the traffic/packet in transit. Moreover, wireless intrusion detection and prevention systems also enable protection of a wireless network by alerting the wireless network administrator in case of a security breach.
Wireless networks are inherently insecure. The out-of-the-box configuration for most wireless networking equipment provided easy (but insecure) access to a wireless network.
We need to understand that wireless networks are generally not as secure as wired networks. Wired networks send data between two points which are connected by a network cable. And wireless networks broadcast data in every direction to every device that happens to be listening, within a limited range.
The following wireless security protocols were developed to protect home wireless networks:
- Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP): The original encryption protocol developed for wireless networks. WEP was designed to provide the same level of security as wired networks. However, WEP has many well-known security flaws, is difficult to configure, and is easily broken.
- Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA): Introduced as an interim security enhancement over WEP while the 802.11i wireless security standard was being developed. Most current WPA implementations use a preshared key (PSK), commonly referred to as WPA Personal, and the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP, pronounced tee-kip) for encryption. WPA Enterprise uses an authentication server to generate keys or certificates.
- Wi-Fi Protected Access version 2 (WPA2): Based on the 802.11i wireless security standard, which was finalized in 2004. The most significant enhancement to WPA2 over WPA is the use of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for encryption. The security provided by AES is sufficient (and approved) for use by the U.S. government to encrypt information classified as top secret.
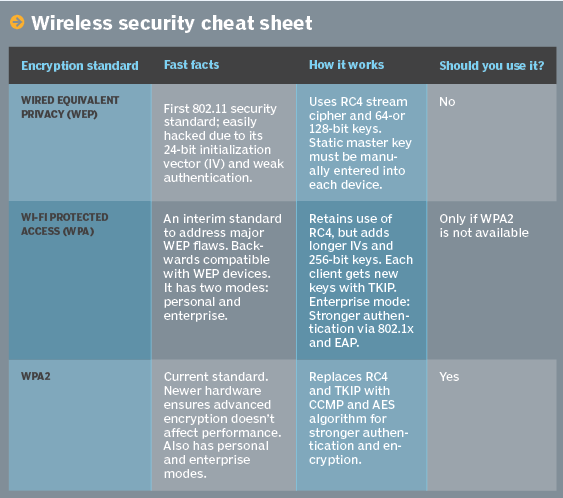
In addition to preventing uninvited guests from connecting to your wireless network, wireless security protocols encrypt your private data as it is being transmitted over the airwaves.
Here is a video I made that shows 5 fundamentals of network security:
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wireless_security
https://www.csoonline.com/article/2122635/mobile-security/wireless-security–the-basics.html
https://www.techopedia.com/definition/29915/wireless-network-security